Fast Facts![]()
| Color | Rabbits range in color from a light brown to a darker gray. |
| Size | 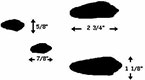
Adults are between 14-18″ long, and weigh up to four pounds. Rabbit tracks are under 1″ in the front and around 3″ in the back. The big rear feet hit the ground in front of the two small front feet as the rabbit moves, leaving a trail that looks like a series of “C”s or “V”s made by the feet. |
| Appearance | The rabbit’s long ears give it the ability to hear noises from all directions, helping them hear predators coming. |
Rabbit Diet
The diet of the rabbit includes vegetation, veggies, grass, herbs, buds, sprouts, and shoots of woody plants including, alfalfa, clover, peas, beans, and grass.
Rabbit Habitat
Rabbits usually place their nests in plain view, sometimes in the middle of a yard, brush piles, or long grass with fur over and around the nest. Other places include wooded, thick brush areas, farmland, orchards, back yards, or hollow logs.
Rabbit Life Cycle
Mating occurs from February to August. The female makes a nest by scraping out a shallow depression in the ground and lining it with grass and her own fur. Females are able to mate almost immediately after giving birth, which allows them to have two to three litters per year with three to six young in each. Young cottontails are born naked, blind, and almost totally helpless, weighing only about one ounce and measuring just four inches in length. They get very little attention from their mother, as she only returns occasionally to the nest to nurse them, but they develop rapidly. Their eyes are open at two weeks, and at four or five weeks, they are weaned and independent. The life expectancy is four to six months old in the wild.
Rabbit Damage & Disease
The most damage rabbits cause is eating out of gardens and destroying yards with digging. In regards to diseases, rabbits can be infested by a number of parasites, including ticks and mites.
Rabbit Prevention & Control
Rabbit Prevention
Like many pests, the best way to get rid of them is to make changes to your home and property to eliminate hiding places for rabbits. This means doing things like:
- Removing brush piles, weed patches, stone piles, and other debris.
- Sealing up areas beneath your deck or porch.
Rabbit Control
Much of wildlife control is knowing and understanding the habitat and behavior of the animal. For rabbits, Batzner uses live trapping with brussel sprouts, carrots, and lettuce.
If you’re having problems with rabbits around your home or business, contact a pest control professional for expert removal services.
Need help with Rabbits?
We'll call you! Leave your information below.





